Ships
Type of resources
Available actions
Topics
Keywords
Contact for the resource
Provided by
Years
Update frequencies
status
-
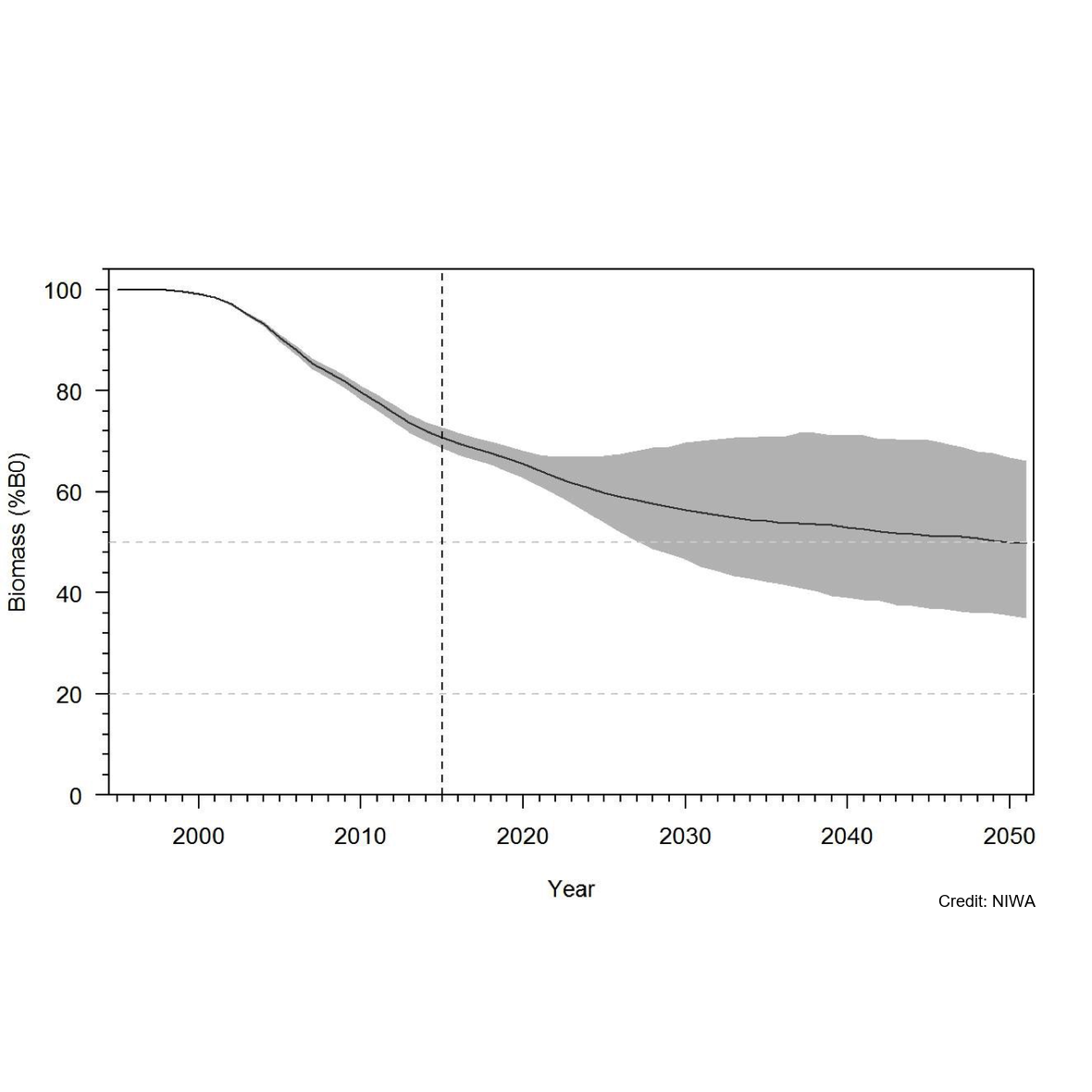
Knowledge of recruitment dynamics, and in particular trends in recruitment and recruitment variability, are key inputs for integrated assessments of fish stocks. A quantitative longline survey monitoring the recruitment of Antarctic toothfish (Dissotichus mawsoni) in the southern Ross Sea was started in 2012. The survey was expanded in 2016 to monitor trends and biological characteristics in two areas of importance to predators, Terra Nova Bay and McMurdo Sound, and to collect data that would contribute to the research and monitoring plan for the Ross Sea region Marine Protected Area. In most years, the survey was completed as planned, while in three years several factors have constrained the survey from sampling all stations and in the latest two seasons pandemic travel restrictions have necessitated an alternative delivery approach. Between 2012 and 2022, 2 056 tagged Antarctic toothfish have been released on the survey and 21 toothfish have been recaptured. Fifteen pop-up satellite archival tags (PSATs) were deployed on D. mawsoni in 2019 and fifteen skates were tagged in 2020 and 2021. Many tagged toothfish released from the RSSS move from the shelf to the slope. Trends in abundance indices and size and age composition consistently show the progression of strong year classes entering and leaving the survey area and have indicated that recruitment is likely more variable than previously thought. Data from the RSSS have been used to indicate year class strength in Antarctic toothfish stock assessments since 2015. The twelve surveys to date have resulted in a substantive increase in the knowledge and understanding of the distribution and relative abundance of a range of demersal fish species and invertebrate taxa caught on the longlines. Other data routinely collected on the surveys were plankton, temperature, salinity, air quality, cetacean and other marine mammal observations, and photo, video, and echosounder data. The RSSS has provided synergies with other research programmes also addressing CCAMLR objectives, particularly those focused on research and monitoring within the RSrMPA. GET DATA: https://www.ccamlr.org/en/publications/statistical-bulletin
-
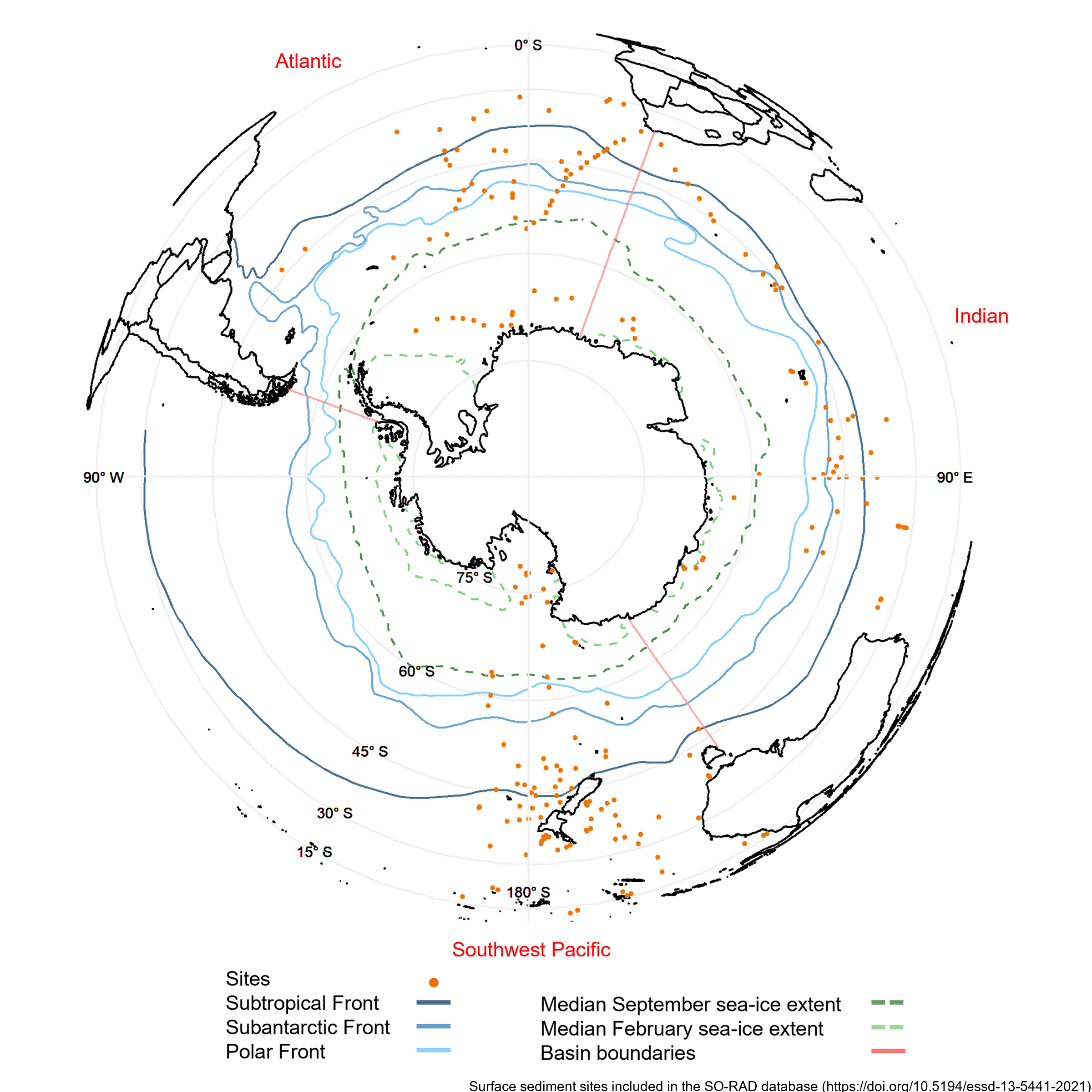
Radiolarians (holoplanktonic Protozoa) found in marine sediments are commonly used in Southern Ocean as palaeoclimate proxies. Generating such reconstructions of past climate based on radiolarian abundances requires a spatially and environmentally comprehensive reference dataset of modern radiolarian census counts. The Southern Ocean RADiolarian (SO-RAD) dataset includes census counts for 237 radiolarian taxa from 228 surface sediment samples located in the Atlantic, Indian and South-west Pacific sectors of the Southern Ocean. This compilation is the largest radiolarian census dataset derived from surface sediment samples in the Southern Ocean. The SO-RAD dataset may be used as a reference dataset for palaeoceanographic reconstructions, or for studying modern radiolarian biogeography and species diversity. RELATED PUBLICATION: https://doi.org/10.5194/essd-13-5441-2021
-
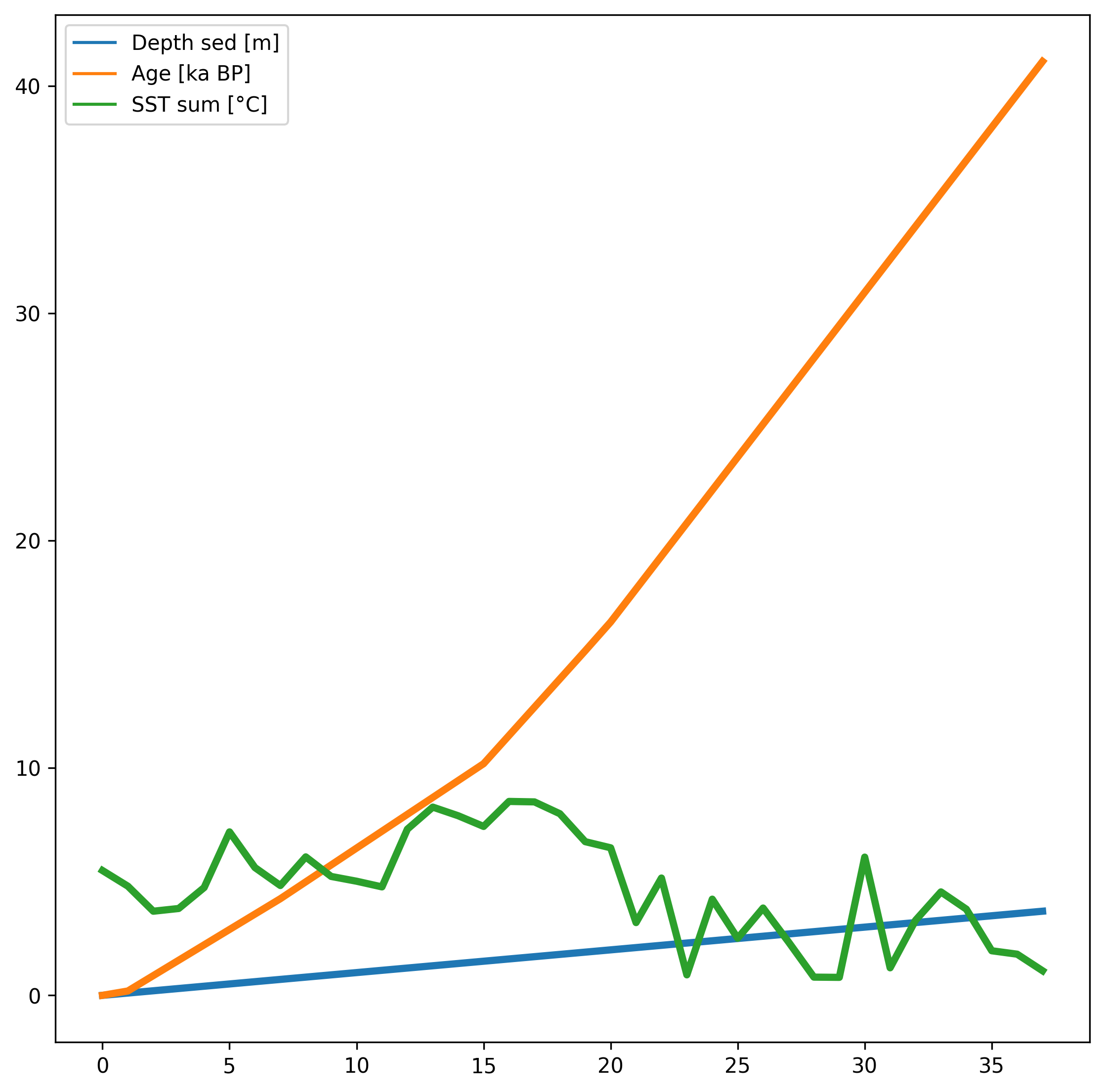
Diatom census counts were used to quantitatively estimate summer sea-surface temperatures (SST) over the last 40,000 years in core MD11-3353, collected in 2011 on board the R.V. Marion Dusfresne west of Kerguelen Island, Southern Ocean. The transfer function used to reconstruct summer (January to March) SST is the Modern Analog Technique that here uses 249 surface sediment samples (modern analogs), the relative abundances of 32 diatom species and the chord distance to select the five most similar modern analogs (Crosta et al., 2020). This method yields a root mean square error of prediction of ~1 °C. The core chronology is detailed in Thöle et al. (2019). RELATED PUBLICATION: Civel-Mazens, Matthieu; Crosta, Xavier; Cortese, Giuseppe; Michel, Elisabeth; Mazaud, Alain; Ther, Olivier; Ikehara, Minoru; Itaki, Takuya (2021): Impact of the Agulhas Return Current on the oceanography of the Kerguelen Plateau region, Southern Ocean, over the last 40 kyrs. Quaternary Science Reviews, 251, 106711, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.quascirev.2020.106711
-

The data set contains water temperature, salinity, and oxygen taken by CTD during three hydrographic sections perpendicular to the slope in the Western Ross Sea between Cape Adare and the Drygalski Trough. Data are in NetCDF. RELATED PUBLICATION: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-021-81793-5 GET DATA: https://www.ncei.noaa.gov/archive/accession/0219916
-

Here we present physico-chemical data collected during two research cruises conducted to and across the Ross Sea, Antarctica in the summer of 2018 (February-March) and 2019 (January-February). The dataset includes measurements of temperature, salinity, oxygen, par and transmissivity obtained with a Sea-Bird Electronics (SBE) 911plus CTD. The CTD sensor was configured with SBE 3plus, SBE 4, and SBE 43 dual sensors for the parameters above, in addition to a seapoint fluorescence sensor, and a photosynthetically active radiation (PAR) sensor (Biospherical Instruments QCP‐2300L‐HP). These data were used to provide oceanographic context to DNA metabarcoding analysis of 18S rRNA V4 region that was carried out on DNA samples collected in parallel to nutrient and chlorophyll-a samples. Fastq samples from DNA metabarcoding analysis and the associated metadata (including nutrients, Chlorophyll-a, and size-fractionated chlorophyll-a) were deposited to GenBank under project numbers PRJNA756172 (2018 cruise) and PRJNA974160 (2019 cruise). The study resulting from this analysis has been submitted to Limnology and Oceanography. RELATED PUBLICATION: Cristi, A., Law, C.S., Pinkerton, M., Lopes dos Santos, A., Safi, K. and Gutiérrez-Rodríguez, A. (2024). Environmental driving forces and phytoplankton diversity across the Ross Sea region during a summer–autumn transition. Limnol Oceanogr. https://doi.org/10.1002/lno.12526
-
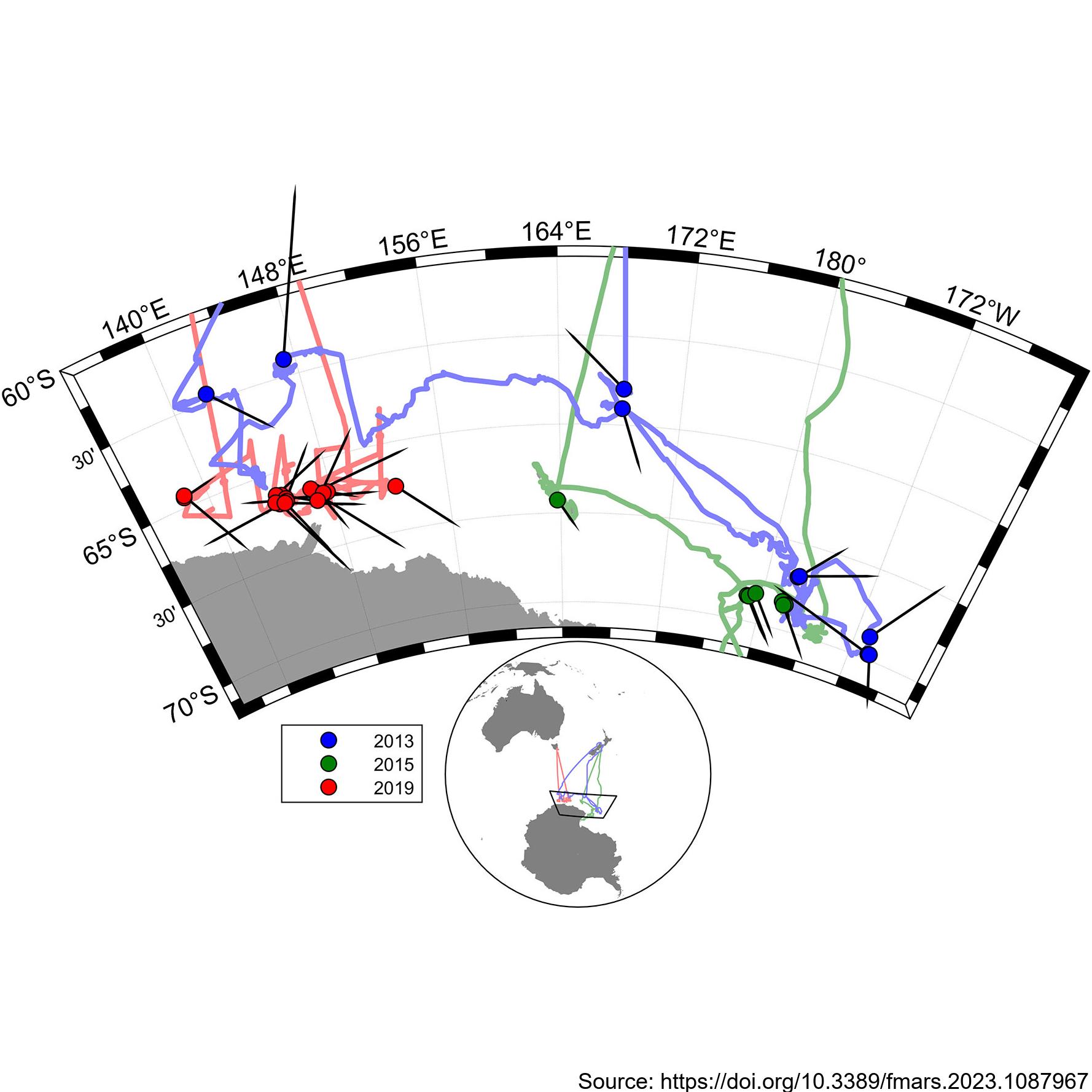
During the 2019 ENRICH Voyage of the CSIRO vessel, RV Investigator, a digital photogrammetric video tracking system was used to collect precise surfacing locations during encounters with mainly Antarctic blue whales, but also some fin whales. The photogrammetric video tracking system is a modern digital video version based on the same operating principle as the that described by Leaper and Gordon 2001, and enables determination of the range and bearing to tracked objects relative to the ship. Video tracking was conducted on 24 occasions for a total of 18 hours. Focal follows were aborted when it was no longer possible to follow the focal animal due to ice or when the presence of other animals meant it was no longer possible to be sure which was the focal animal. Calderan SV, Leaper R, Andrews-Goff V, Miller BS, Olson PA, Reyes MVR, Bell E and Double MC (2023) Surfacing rates, swim speeds, and patterns of movement of Antarctic blue whales. Front. Mar. Sci. 10:1087967. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmars.2023.1087967 GET DATA: https://doi.org/10.26179/tcbe-4h63
 GeoData.NZ
GeoData.NZ