ASP
Type of resources
Available actions
Topics
Keywords
Contact for the resource
Provided by
Years
Update frequencies
status
-
AntAir ICE is an air temperature dataset for terrestrial Antarctica, the ice shelves, and the seasonal sea ice around Antarctica in a 1km2 spatial grid resolution and a daily temporal resolution available from 2003-2021. AntAir ICE was produced by modelling air temperature from MODIS ice surface temperature and land surface temperature using linear models. In-situ measurements of air temperature from 117 Automatic Weather Stations were used as the response variable. Each day has a bricked spatial raster with two layers, saved as a GeoTIFF format and in the Antarctic Polar Stereographic projection (EPSG 3031). The first layer is the predicted near surface air temperature for that day in degree Celsius * 10 and the second layer is the number of available MODIS scenes for that day ranging from 0 to 4. Areas with cloud contamination or without sea ice are marked with no data. Files for each year (2003-2021) are compressed with a ZIP files for each quarter. Python 3.8 was used for conversion of the MODIS products from HDF files to raster and all data handling and processing was thereafter done in R version 4.0.0. All data processing and modelling procedures are available as R scripts on a public Github repository: https://github.com/evabendix/AntAir-ICE. Using this code it is possible to download new available MODIS LST and IST scenes and apply the model to continue the near-surface air temperature dataset. Related Publication: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41597-023-02720-z GET DATA: https://doi.org/10.1594/PANGAEA.954750
-

This metadata record represents the R phytoclass package. Determine the chlorophyll a (Chl a) biomass of different phytoplankton groups based on their pigment biomarkers. The method uses non-negative matrix factorisation and simulated annealing to minimise error between the observed and estimated values of pigment concentrations (Hayward et al. (2023) https://doi.org/10.1002/lom3.10541). The approach is similar to the widely used 'CHEMTAX' program (Mackey et al. 1996) https://doi.org/10.3354/meps144265), but is more straightforward, accurate, and not reliant on initial guesses for the pigment to Chl a ratios for each phytoplankton group. Further details are provided at: Hayward, A., M. H. Pinkerton, and A. Gutierrez-Rodriguez. 2023. phytoclass: A pigment-based chemotaxonomic method to determine the biomass of phytoplankton classes. Limnol. Oceanogr. Methods 21: 220–241. https://doi.org/10.1002/lom3.10541 GET PACKAGE: https://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/phytoclass/readme/README.html
-
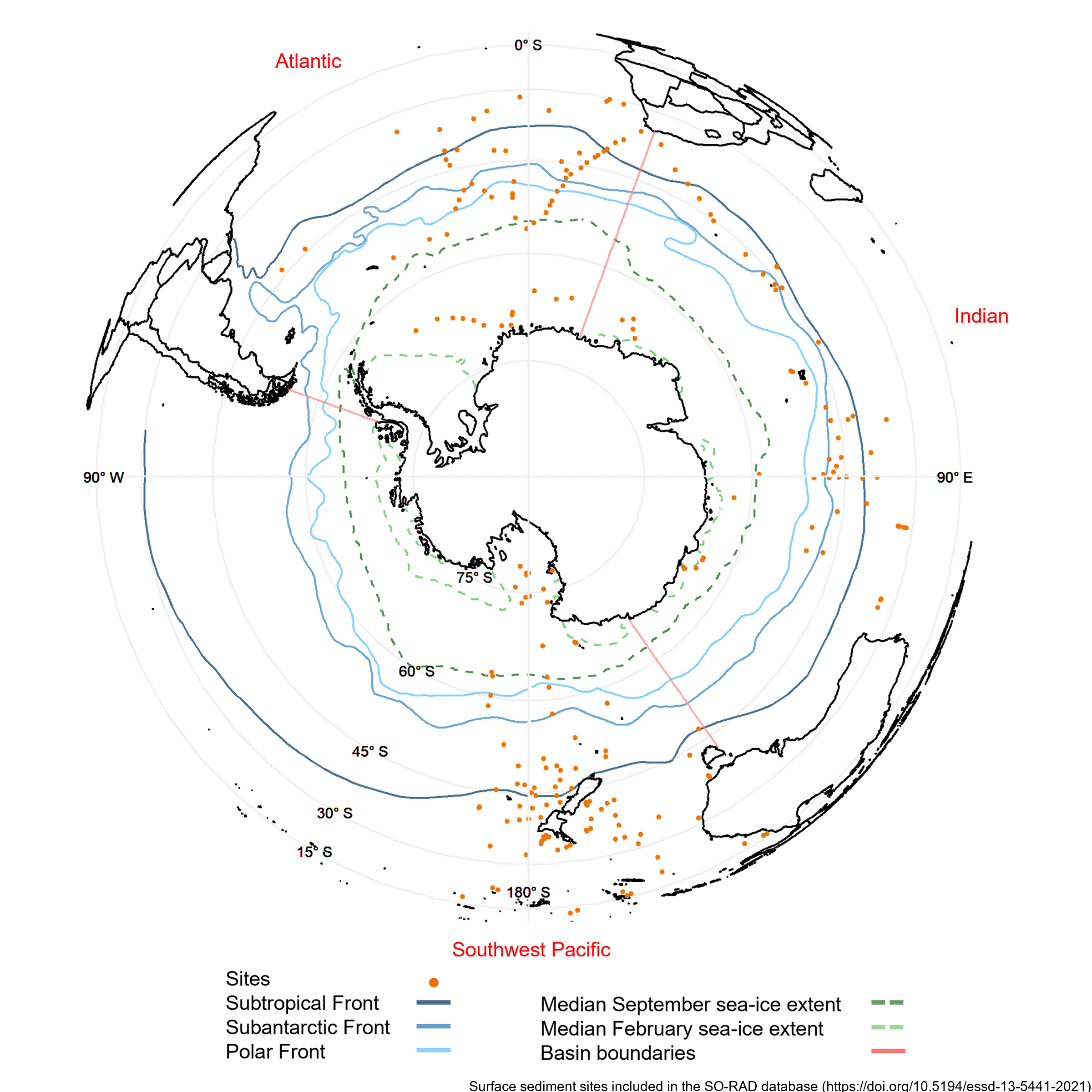
Radiolarians (holoplanktonic Protozoa) found in marine sediments are commonly used in Southern Ocean as palaeoclimate proxies. Generating such reconstructions of past climate based on radiolarian abundances requires a spatially and environmentally comprehensive reference dataset of modern radiolarian census counts. The Southern Ocean RADiolarian (SO-RAD) dataset includes census counts for 237 radiolarian taxa from 228 surface sediment samples located in the Atlantic, Indian and South-west Pacific sectors of the Southern Ocean. This compilation is the largest radiolarian census dataset derived from surface sediment samples in the Southern Ocean. The SO-RAD dataset may be used as a reference dataset for palaeoceanographic reconstructions, or for studying modern radiolarian biogeography and species diversity. RELATED PUBLICATION: https://doi.org/10.5194/essd-13-5441-2021
-
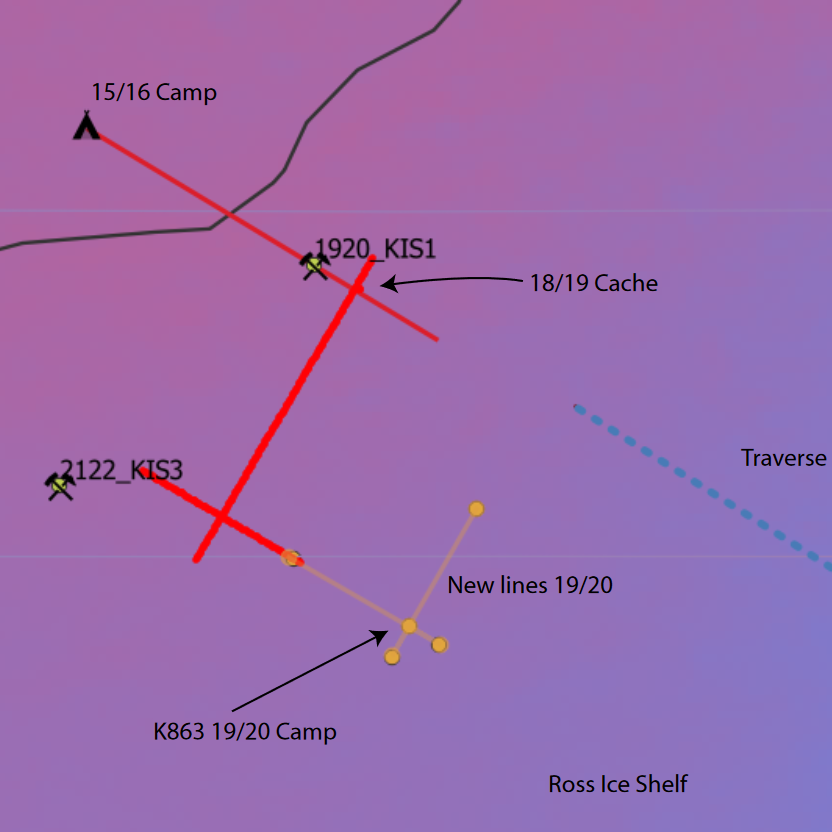
These data are described in detail by 'Melting and refreezing in an ice shelf basal channel at the grounding line of the Kamb Ice Stream. ApRES observations were made in December 2019 and repeated in December 2020 at the same locations. Data collection and processing followed the method described in Stewart et al. (2019). ApRES dataset.zip' contains raw ApRES data and processed results from a spatial survey of basal mass balance - detailed in Sections 2.2.4 and 3.2.2 of https://doi.org/10.1029/2021JF006532. GET DATA: https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.5574647
-
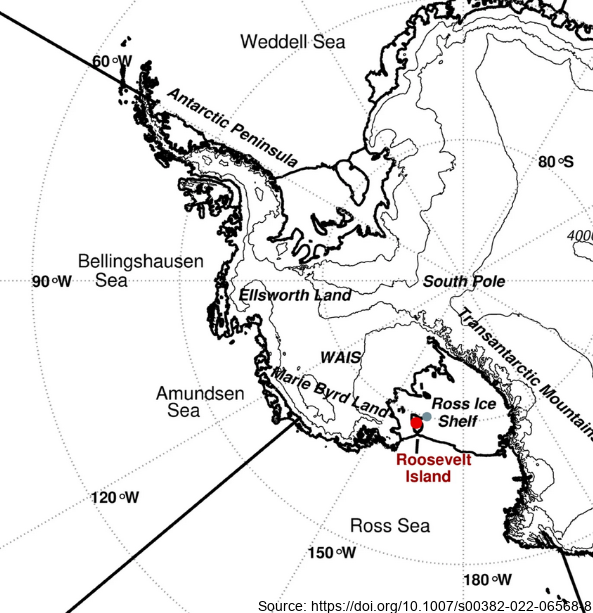
Here we examine the water stable-isotope data from the Roosevelt Island Climate Evolution (RICE) ice core. In this study, we use empirical orthogonal function (EOF) analysis to investigate the relationship between RICE ice-core oxygen-18 isotopes (δ18O) and Southern Hemisphere atmospheric circulation during the extended austral winter (April–November). - Deep Location: 79.364°S, 161.706°W, elevation 550 m a.s.l. - 12/13B Location: 79.362°S, 161.698°W, elevation 550 m a.s.l. - Core depth 763 m. Depth interval provided here: 1.29 to 38.56 m - txt data file, NaN = no data Further details are available at https://doi.org/10.1007/s00382-022-06568-8 GET DATA: https://github.com/demanuelsson/ClimDyn_2022_Matlab/tree/main/data
-

Plot data Mc Nemar: To enable comparisons with the 1961 and 2004 survey results, the Lambert Conformal Conic projection from the 2004 survey was used to precisely georeference and trim the RGB image across a 1-m2 grid, generating a total of 3,458 1-m2 grid cells. For each grid cell moss, lichen, or algae/cyanobacteria cover was extracted as one of the four cover classes: Heavy (>40%), Patchy (10–40%), Scattered (less than 10%), and None (0%) for the survey years 1962, 2004 and 2018. Ground truthing: To test the overall accuracy of cover classifications and ensure consistency with 2004 survey methodologies, a ground-truthing approach was performed. Photographs were taken of individual cells along eight transects, running west to east across the plot at 0.5, 1.5, 15.5, 16.5, 28.5, 29.5, 116.5 and 117.5 m distance from the NW corner. Each grid cell could be identified individually with an x/y coordinate in the centre and was surrounded by a rectangular frame parallel to the outer edge of the plot. A total of 174 photographs were taken and archived with Antarctica New Zealand. For each photographed grid cell, the presence of each functional group of vegetation and their cover class was assessed visually. Orthomosaic image: Aerial images were obtained using a DJI Matrice 600 Pro hex-rotor remotely piloted aircraft system equipped with a Canon EOS 5Ds camera (image size: 8688×5792 pixels, focal length: 50 mm, pixel size: 4.14 μm) on November 28, 2018. The flight altitude was 30 m above ground level, and a total of 10 ground-control points were included to provide accurate geo-referencing. An orthomosaic photo and accompanying DEM was generated with the acquired aerial images using Agisoft PhotoScan (now known as Metashape by Agisoft LLC, https://www.agisoft.com/) RELATED PUBLICATION: https://doi.org/10.1029/2022EF002823 GET DATA: https://doi.org/10.7488/ds/3417
-
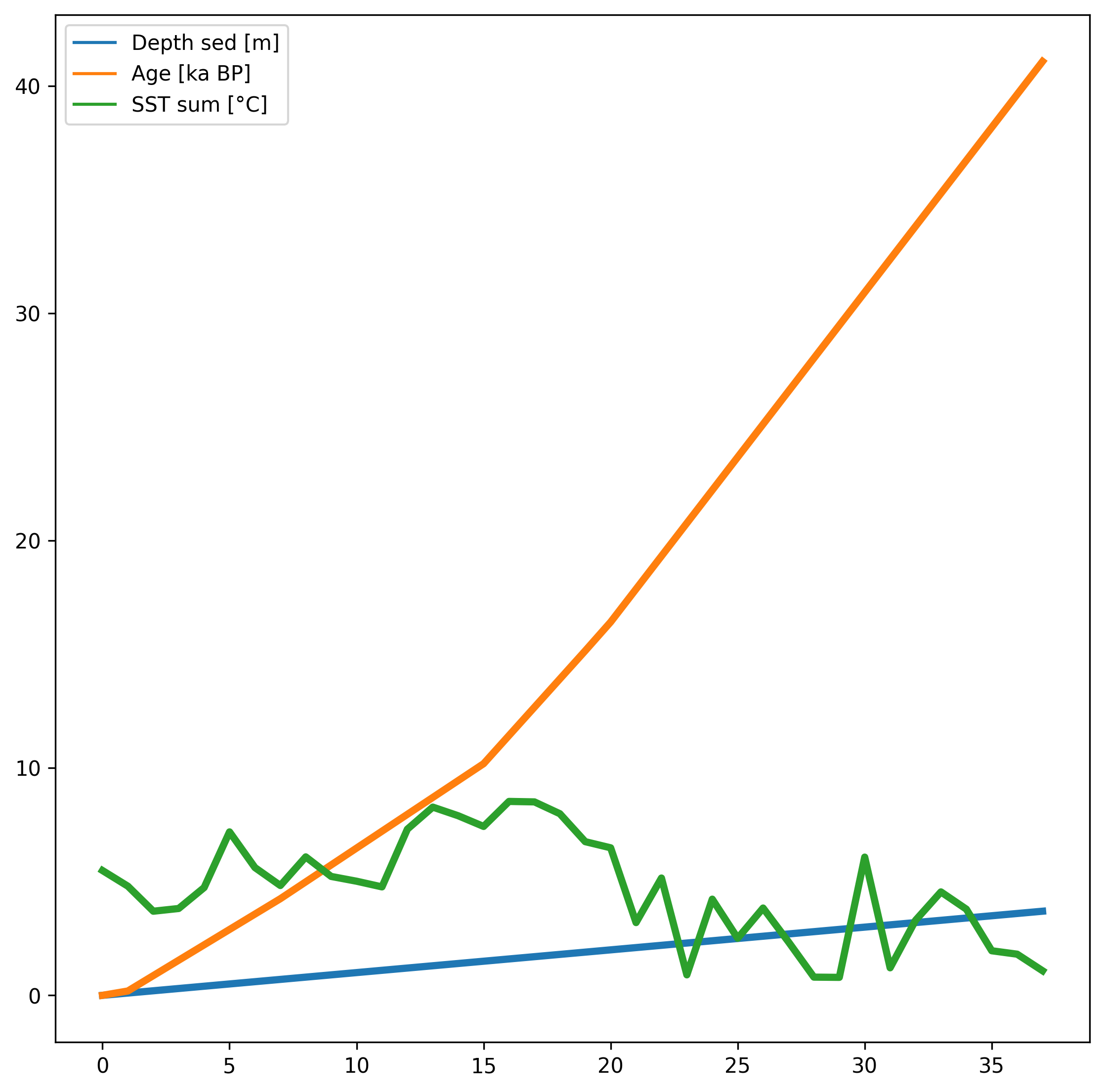
Diatom census counts were used to quantitatively estimate summer sea-surface temperatures (SST) over the last 40,000 years in core MD11-3353, collected in 2011 on board the R.V. Marion Dusfresne west of Kerguelen Island, Southern Ocean. The transfer function used to reconstruct summer (January to March) SST is the Modern Analog Technique that here uses 249 surface sediment samples (modern analogs), the relative abundances of 32 diatom species and the chord distance to select the five most similar modern analogs (Crosta et al., 2020). This method yields a root mean square error of prediction of ~1 °C. The core chronology is detailed in Thöle et al. (2019). RELATED PUBLICATION: Civel-Mazens, Matthieu; Crosta, Xavier; Cortese, Giuseppe; Michel, Elisabeth; Mazaud, Alain; Ther, Olivier; Ikehara, Minoru; Itaki, Takuya (2021): Impact of the Agulhas Return Current on the oceanography of the Kerguelen Plateau region, Southern Ocean, over the last 40 kyrs. Quaternary Science Reviews, 251, 106711, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.quascirev.2020.106711
-
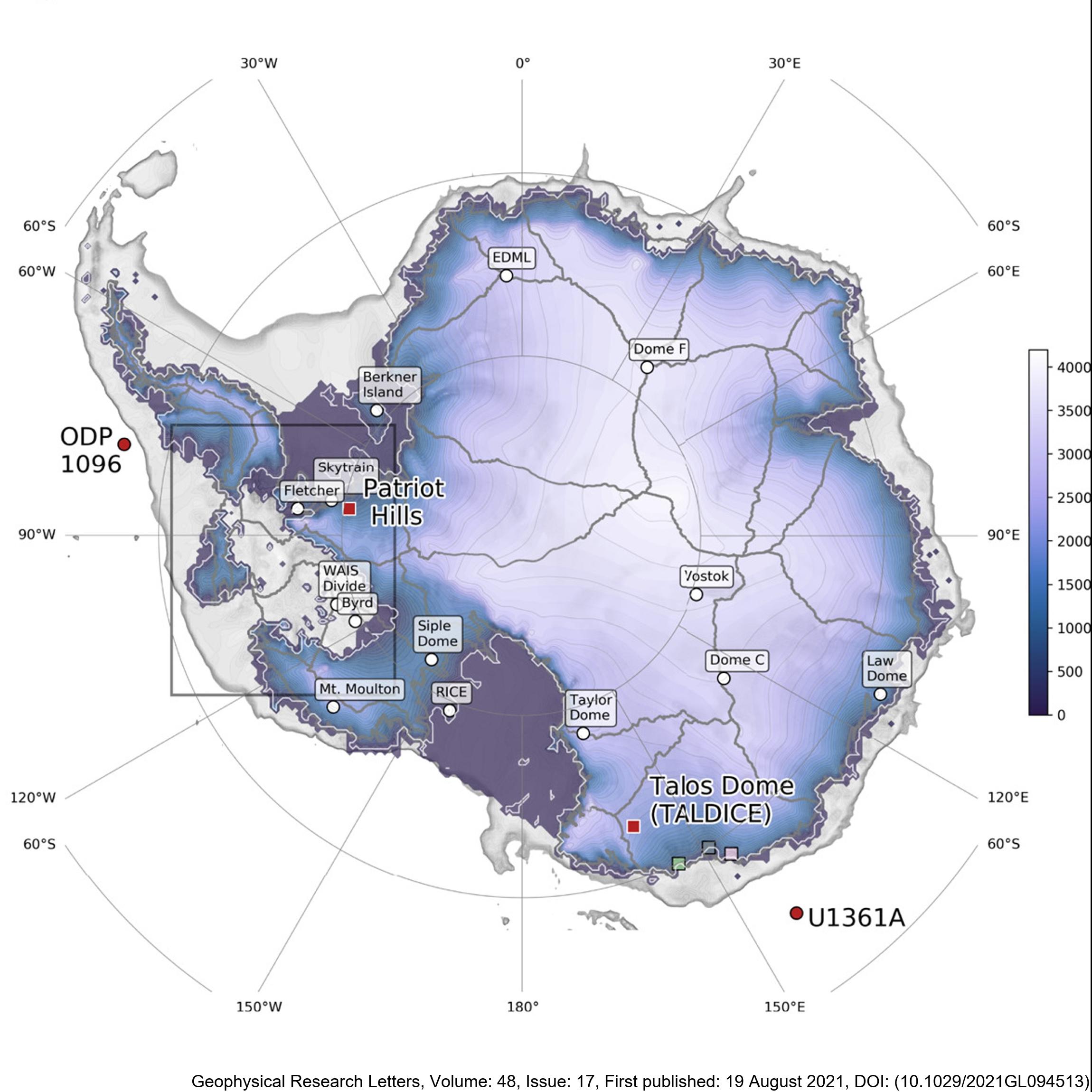
Here, we present new, transient, GCM-forced ice-sheet simulations validated against proxy reconstructions. This is the first time such an evaluation has been attempted. Our empirically constrained simulations indicate that the AIS contributed 4 m to global mean sea level by 126 ka BP, with ice lost primarily from the Amundsen, but not Ross or Weddell Sea, sectors. We resolve the conflict between previous work and show that the AIS thinned in the Wilkes Subglacial Basin but did not retreat. We also find that the West AIS may be predisposed to future collapse even in the absence of further environmental change, consistent with previous studies. There are two files, for Termination 1 ('T1') and Termination 2 ('T2'). They contain spatial fields for ice thickness, ice surface elevation, bedrock elevation, surface and basal velocity, and mask. The T1 outputs are every 500 years, whereas the T2 outputs are every 100 years. The spatial resolution of both is 20 km. Sea-level-equivalent mass loss can be calculated from these outputs, but is also provided here in a text file for convenience. RELATED PUBLICATION: Golledge, N.R., Clark, P.U., He, F., et al. (2021). Retreat of the Antarctic Ice Sheet During the Last Interglaciation and Implications for Future Change. Geophysical Research Letters, 48(17). https://doi.org/10.1029/2021GL094513 GET DATA: https://doi.org/10.17605/OSF.IO/GZB3H
-

Here, we present a decadally resolved record of sea-salt sodium (a proxy for open-ocean area) and non-sea salt calcium (a proxy for continental dust) from the well-dated Roosevelt Island Climate Evolution (RICE) core, focusing on the time period between 40–26 ka BP. Drilling site coordinates: (79.364° S, 161.706°W). Further collection details can be found at https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-023-40951-1
-

In Antarctica, ice shelves such as the Ross Ice Shelf (RIS) fringe 75% of the coastline and cover over 1.5 million km2, creating distinct and largely unexplored marine environments. It is fundamental to characterize the communities under these shelves to understand their biogeochemical role and predict how they might respond to future ice-shelf collapse 1,2. While historical studies suggested the RIS harbors active microorganisms 3–5, nothing is known about the composition of these communities. In this study, we profiled the composition, function, and activities of microbial communities in three seawater samples (400, 550, 700 m depth) underlying the shelf interior. We combined rate measurements with multi-omics (i.e. single-cell genomics, metagenomics, metatranscriptomics, and metaproteomics). Overall, below-shelf waters harbour microbial communities of comparable abundance and diversity to deep pelagic waters. Based on the meta-omic data, the community is inferred to be sustained by dark carbon fixation using ammonia, nitrite, and sulfur compounds as electron donors. In turn, these chemolithoautotrophs are predicted to support the aerobic heterotrophic majority and various trophic interactions. Consistently, this study and previous activity measurements suggest that dark carbon fixation is sufficient to sustain prokaryotic heterotrophic production, making the waters below the RIS presumably the largest chemolithotrophic system in the global ocean. Further details are provided at https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-021-27769-5 GET DATA: https://www.ebi.ac.uk/ena/browser/view/PRJEB35712 GET DATA: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/bioproject/?term=PRJNA593264
 GeoData.NZ
GeoData.NZ